In every lab, whether it’s a clinical lab, research lab, educational lab, industrial lab, or diagnostic lab, precision and efficiency start with having the right consumables available. From tubes that protect your precious samples to the tips that dispense microliter volumes of liquids, these humble products are the backbone of every lab. Under the category of Lab Supplies & Consumables, a variety of products are brought together that are important for accuracy, consistency, and safety in every scientific setup.
These are not just accessories, but the workhorses of scientific processes.They keep your experiments on track and your results accurate. With products engineered for compatibility, durability, and usability, today’s labs rely on a wide range of products such as tubes and vials, liquid handling equipment, microplates, plasticware, glassware, labels and organization supplies, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Why Consumables Matter in Labs
The unsung heroes of science are consumables. While machines such as centrifuges and spectrophotometers receive greater prominence, the reality is that consumables are what make these machines perform optimally. Consumables help in:
-
Sample integrity and safety during processing and storage.
-
Accuracy in measurement and transfer of liquids and reagents.
-
Consistent experimental conditions, especially in high-throughput assays like ELISAs and PCR.
-
Clean and organized workflow that enhances productivity and reduces errors.
Regardless of whether scientists are working against the clock or are working in bulk, the quality of consumables plays a significant role in the quality of results obtained.
Tubes & Vials
One of the most basic and important consumable items, tubes and vials are the unsung heroes of sample collection, transportation, storage, and processing of biological or chemical materials. In any laboratory, various types of tubes are required depending on the process or procedure:
Microcentrifuge Tubes
These are small tubes, usually of 0.5 mL, 1.5 mL, or 2.0 mL volume, microcentrifuge compatible. They are used in order to perform a quick centrifugation step in DNA preparation, in storing reagents of small volume, or in purifying proteins.
Centrifuge Tubes
These are larger tubes, usually with a volume of 15 mL or 50 mL. These tubes are required for suspending cells, separating phases, or handling larger volumes of fluid.
Cryogenic Storage Vials
These tubes are needed to store samples that are stored in liquid nitrogen or cryogenic freezers, for preserving viability and for long-term studies.
Specialized Tube Caps & Racks
The selection of tubes is based on a variety of factors, such as the material used for the tube, whether it is plastic or made of glass, and the downstream process.
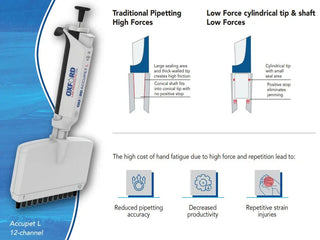
Pipettes & Pipette Tips
Liquid handling is the center of virtually every laboratory procedure, and pipettes are the key to accurate and reproducible results.
Manual and Multichannel Pipettes
-
For single-channel sample handling, single-channel pipettes are the best option.
-
For parallel liquid handling, multichannel pipettes are the way to go.
Pipette Tips
Pipette tips are essential for the procedure, providing precise and clean data, and come in different sizes, such as 10 µl, 200 µl, and 1000 µl.
Reservoirs & Controllers
Reservoirs and controllers are accessories to the pipettes, providing convenient liquid handling and comfortable handling, thus reducing the strain on the user.
The accuracy and precision of the results are ensured by the quality of the pipettes and the tips, providing the laboratory with the results it needs to be able to trust.
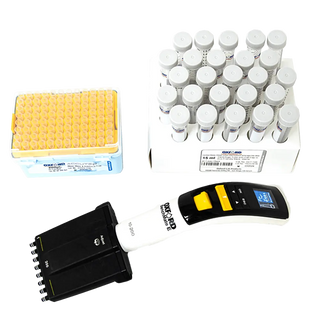
Microplates
Microplates are employed in high-throughput screening, enzyme analysis, PCR, ELISA analysis, and numerous other procedures. This enables several reactions or analyses to be conducted simultaneously in one container.
96-Well & 384-Well Formats
Microplates are used for high-throughput screening, enzyme assays, PCR reactions, ELISA tests, and many other applications. This allows for multiple reactions or measurements to occur simultaneously within one vessel.
PCR Plates
PCR plates are used for thermal cycling reactions and are essential for diagnostics, genotyping, and molecular biology.
Plate Seals & Covers
Plate seals are used to prevent evaporation and contamination during incubation or storage.
Microplates are essential for many applications within biotech, pharmaceutical R&D, and clinical laboratories, where volume and consistency are as important as precision.
Glassware & Plasticware
In addition to tubes and tips, many laboratories use a variety of glassware and plasticware for routine activities involving mixing, measuring, culturing, and storing materials.
Laboratory Glassware
Generally, borosilicate glassware such as borosilicate glass beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, graduated cylinders, and volumetric flasks are used. This is because they are transparent, have a high temperature tolerance, and are inert.
Plasticware
Petri dishes and culture plates made of plastic, plastic bottles, plastic graduated cylinders, and plasticware containers are generally used for different purposes in the laboratory. The plasticware containers are made of polypropylene and polystyrene materials. They are generally used in the laboratory because they are inert and transparent.
Inclusive Sample Formats
-
Petri dishes and culture plates are used for microbiology and cell culture.
-
Measuring cylinders and mixing bottles are used for quantitative liquids.
-
Sealed bottles are used for storing liquids.
In selecting laboratory glassware or plasticware, temperature requirements, chemical inertness, and sterilization requirements are considered.
Organization, Tracking & Safety
While consumables refer to containers and tips, it also includes tools that help in maintaining a safe and organized environment in the laboratory.
Racks & Storage Solutions
Tube racks, cryoboxes, and plate holders enable the storage and retrieval of samples in an orderly manner, even in deep freezer storage.
Lab Labels & Marking Tools
Effective labels ensure the traceability of the samples, reducing the risk of mix-ups and quick identification of the workflow.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Gloves, masks, and personal safety gear provide a high degree of security for the personnel from the hazardous materials used in the laboratories, thus helping in the compliance of safety regulations.
Consumable Accessories
Weigh boats, trays, and reagent holders help in the smooth flow of the workflow, and these small items contribute to the safe and efficient working in the laboratories.
How to Choose the Right Consumables
With so many different products out there, it can be difficult to choose the right consumables. Here are some important points to keep in mind:
-
Material Compatibility: Make sure that your materials (plastic vs. glass) are compatible with your needs (chemical resistance, temperature stability).
-
Sterility: When working with sensitive biological materials, sterile and RNase/DNase-free consumables are necessary.
-
Volume & Format: Select consumables with the right number of tubes, plate wells, and tip sizes for your needs.
-
Workflow Integration: Ensure that your consumables are compatible with your equipment (centrifuges, pipettes, plate readers).
-
Durability & Clarity: When using consumables multiple times, high clarity and shock resistance in glassware are necessary.
Balancing these factors leads to better accuracy, less waste, and more efficient operations.
Consumables That Keep Labs Running
From everyday pipette tips to specialized microplates and precision glassware, the Laboratory Supplies & Consumables category represents the everyday essentials that laboratories depend on to get the job done. These supplies represent the foundation upon which accurate science, a safe working environment, and efficient operations depend in a wide range of scientific disciplines from academic research to clinical diagnostics, as well as industry-based quality control and high-throughput screening.
The Laboratory Supplies & Consumables category, when thoughtfully stocked, can play an important role in reducing downtime, preventing mistakes, and giving scientists and technicians everywhere the freedom to do what they do best: discovery, validation, and innovation.